Enhancing precision and control with Selective-Fire Triggers.
How Selective-Fire Triggers Work
Selective-fire triggers are a crucial component in firearms that allow the shooter to choose between different firing modes, such as semi-automatic, burst fire, or fully automatic. Understanding how these triggers work is essential for anyone looking to use firearms safely and effectively.
At its core, a selective-fire trigger is designed to control the rate at which bullets are fired from a firearm. This is achieved by manipulating the trigger mechanism to engage different sear surfaces, which in turn determine the firing mode. In semi-automatic mode, pulling the trigger releases the hammer or striker to fire a single round. In burst fire mode, the trigger is designed to release a predetermined number of rounds with each pull. And in fully automatic mode, the trigger allows for continuous firing until the trigger is released or the ammunition is depleted.
The mechanism behind selective-fire triggers is intricate and requires precise engineering to ensure reliable and safe operation. One common design is the fire control group, which consists of various components such as the trigger, sear, disconnector, and selector switch. When the trigger is pulled, it engages the sear, which holds the hammer or striker in the cocked position. As the trigger is released, the sear disengages, allowing the hammer or striker to strike the firing pin and ignite the primer.
The selector switch is a critical component that allows the shooter to choose between different firing modes. By rotating the selector switch, the shooter can switch between semi-automatic, burst fire, and fully automatic modes. This is achieved by changing the position of the sear surfaces within the trigger mechanism, which determines how the trigger interacts with the hammer or striker.
Understanding the mechanism behind selective-fire triggers is essential for anyone looking to use firearms safely and effectively. By knowing how the trigger operates and how to select the appropriate firing mode, shooters can ensure that they are using their firearms in a responsible and controlled manner.
Applications of selective-fire triggers are diverse and can be found in a wide range of firearms, from military and law enforcement weapons to civilian sporting rifles. In military and law enforcement applications, selective-fire triggers allow for greater flexibility in engaging targets at different ranges and in varying combat scenarios. By being able to switch between semi-automatic, burst fire, and fully automatic modes, soldiers and law enforcement officers can adapt to changing situations quickly and effectively.
In civilian sporting rifles, selective-fire triggers are often used for recreational shooting and competition. Shooters can enjoy the challenge of mastering different firing modes and testing their marksmanship skills in a controlled environment. By understanding how selective-fire triggers work and practicing safe shooting techniques, shooters can enhance their shooting experience and improve their overall proficiency with firearms.
In conclusion, selective-fire triggers are a critical component in firearms that allow shooters to choose between different firing modes. By understanding how these triggers work and how to select the appropriate firing mode, shooters can use their firearms safely and effectively. Whether in military, law enforcement, or civilian applications, selective-fire triggers play a vital role in enhancing shooting performance and versatility.
The History of Selective-Fire Triggers
Selective-fire triggers are a crucial component in firearms that allow the shooter to choose between different firing modes, such as semi-automatic, burst fire, or fully automatic. Understanding how these triggers work and their applications is essential for anyone interested in firearms or gunsmithing.
The history of selective-fire triggers dates back to the early 20th century when the first attempts were made to create firearms that could fire multiple rounds with a single pull of the trigger. The development of selective-fire triggers was driven by the need for more efficient and versatile firearms for military use.
One of the earliest examples of a selective-fire trigger is the M1918 Browning Automatic Rifle (BAR), which was used by the United States military during World War I. The BAR featured a selective-fire trigger that allowed the shooter to switch between semi-automatic and fully automatic firing modes.
Over the years, selective-fire triggers have become more sophisticated and reliable, thanks to advancements in technology and manufacturing processes. Modern selective-fire triggers are designed to be durable, precise, and easy to use, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
One of the key benefits of selective-fire triggers is their versatility. By allowing the shooter to choose between different firing modes, selective-fire triggers can adapt to various shooting scenarios and environments. For example, in a close-quarters combat situation, a shooter may prefer to use fully automatic fire to suppress enemy fire quickly. In contrast, in a long-range engagement, semi-automatic fire may be more appropriate for precision shooting.
Selective-fire triggers are also commonly used in law enforcement and military applications. Police officers and soldiers often need to switch between different firing modes quickly and efficiently, depending on the situation they are facing. Selective-fire triggers allow them to do so with ease, enhancing their effectiveness and safety in the field.
In addition to military and law enforcement applications, selective-fire triggers are also popular among civilian shooters and gun enthusiasts. Many firearms manufacturers offer rifles and handguns with selective-fire triggers for recreational shooting and competition purposes. These firearms allow shooters to experience the thrill of firing in different modes and improve their shooting skills.
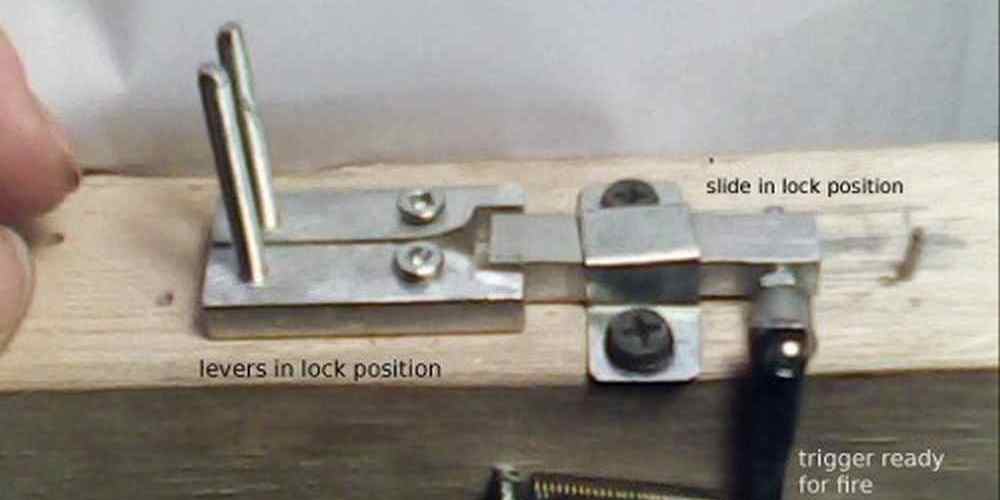
When it comes to understanding the mechanism of selective-fire triggers, it is essential to know how they work. Selective-fire triggers typically consist of a sear, a disconnector, and a selector switch. The sear holds the hammer or striker in place until the trigger is pulled, releasing it to strike the firing pin and ignite the cartridge. The disconnector ensures that the firearm cycles correctly between shots, preventing the hammer from falling until the trigger is released. The selector switch allows the shooter to choose between different firing modes by adjusting the position of the sear and disconnector.
In conclusion, selective-fire triggers are a vital component in firearms that offer shooters the flexibility to choose between different firing modes. Whether used in military, law enforcement, or civilian applications, selective-fire triggers enhance the versatility and effectiveness of firearms. Understanding how selective-fire triggers work and their applications is essential for anyone interested in firearms or gunsmithing.
Different Types of Selective-Fire Triggers
Selective-fire triggers are a crucial component in firearms that allow the shooter to choose between different firing modes, such as semi-automatic, burst fire, or fully automatic. Understanding how these triggers work and their various applications is essential for anyone looking to improve their shooting skills or knowledge of firearms.
One of the most common types of selective-fire triggers is the two-stage trigger. This type of trigger has two distinct stages of pull before the shot is fired. The first stage, known as the take-up stage, involves pulling the trigger until it reaches a stopping point. The second stage, known as the break stage, requires additional pressure to be applied to the trigger before the shot is fired. This design helps to improve accuracy by allowing the shooter to take up the slack in the trigger before applying the final pressure needed to fire the weapon.
Another type of selective-fire trigger is the binary trigger. Binary triggers are unique in that they allow the shooter to fire a round both when the trigger is pulled and released. This means that the shooter can fire two rounds with a single pull of the trigger, making it an excellent option for rapid-fire shooting. Binary triggers are popular among competitive shooters and enthusiasts who enjoy the thrill of shooting quickly and accurately.
In addition to two-stage and binary triggers, there are also other types of selective-fire triggers, such as the three-round burst trigger. This type of trigger allows the shooter to fire three rounds with a single pull of the trigger, making it a versatile option for both semi-automatic and burst fire modes. Three-round burst triggers are commonly used in military and law enforcement applications where controlled bursts of fire are necessary.
Understanding the different types of selective-fire triggers and their applications is essential for anyone looking to improve their shooting skills or knowledge of firearms. Whether you are a competitive shooter, law enforcement officer, or firearms enthusiast, having a solid understanding of how selective-fire triggers work can help you make informed decisions when selecting a firearm for your needs.
In conclusion, selective-fire triggers are a critical component in firearms that allow the shooter to choose between different firing modes. By understanding the various types of selective-fire triggers and their applications, you can improve your shooting skills and knowledge of firearms. Whether you prefer a two-stage trigger for improved accuracy, a binary trigger for rapid-fire shooting, or a three-round burst trigger for controlled bursts of fire, there is a selective-fire trigger option to suit your needs. So next time you are looking to upgrade your firearm or learn more about selective-fire triggers, remember to consider the different types available and how they can enhance your shooting experience.
Legal Considerations for Selective-Fire Triggers
Selective-fire triggers are a crucial component of firearms that allow the shooter to choose between different firing modes, such as semi-automatic, burst fire, or fully automatic. Understanding how these triggers work and their legal implications is essential for gun owners and enthusiasts alike.
In the United States, the National Firearms Act (NFA) regulates the possession and use of selective-fire triggers, also known as machine guns. Under the NFA, machine guns are defined as firearms that can fire more than one shot with a single pull of the trigger. This includes firearms that have been modified to function as fully automatic weapons.
To legally own a machine gun in the United States, individuals must obtain a special license from the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF). This process involves a thorough background check, fingerprinting, and payment of a tax stamp. Once approved, owners must adhere to strict regulations regarding the storage, transportation, and use of their machine gun.
It is important to note that not all selective-fire triggers are considered machine guns under the NFA. Some firearms, such as the AR-15, have a selector switch that allows the shooter to switch between semi-automatic and fully automatic modes. These firearms are classified as “select-fire” weapons and are subject to different regulations than machine guns.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in aftermarket trigger modifications that can enhance the performance of firearms. These modifications, such as bump stocks and binary triggers, can increase the rate of fire and improve accuracy. However, the legality of these modifications is a subject of debate.
In 2018, the ATF reclassified bump stocks as machine guns, effectively banning their sale and possession in the United States. This decision was made in response to the mass shooting in Las Vegas, where the shooter used a bump stock to increase the rate of fire of his semi-automatic rifle. The ban on bump stocks has raised questions about the legality of other trigger modifications and their potential impact on gun control laws.
Despite the controversy surrounding selective-fire triggers, they have legitimate applications in law enforcement and military settings. Police officers and military personnel often use firearms with selective-fire triggers to respond to threats quickly and effectively. These triggers allow them to switch between different firing modes depending on the situation, giving them a tactical advantage in high-pressure scenarios.
In conclusion, understanding the mechanism and legal considerations of selective-fire triggers is essential for gun owners and enthusiasts. While these triggers have legitimate applications in law enforcement and military settings, they are subject to strict regulations under the NFA. It is important for individuals to educate themselves on the laws surrounding machine guns and other trigger modifications to ensure compliance and safety. By staying informed and following the proper procedures, gun owners can enjoy their firearms responsibly and legally.
Applications of Selective-Fire Triggers in Firearms
Selective-fire triggers are a crucial component in firearms that allow shooters to choose between different firing modes, such as semi-automatic, burst fire, or fully automatic. Understanding how these triggers work and their applications can help gun enthusiasts and professionals make informed decisions when selecting firearms for specific purposes.
In semi-automatic mode, a single round is fired each time the trigger is pulled. This mode is commonly used for precision shooting and target practice, as it allows for accurate and controlled shots. Semi-automatic firearms are popular among hunters and sports shooters due to their ease of use and reliability.
Burst fire mode, on the other hand, allows for a predetermined number of rounds to be fired with a single pull of the trigger. This mode is often used in military and law enforcement applications, as it provides a balance between the controlled shots of semi-automatic mode and the rapid fire of fully automatic mode. Burst fire triggers are designed to ensure consistent and reliable performance in high-stress situations.
Fully automatic mode allows for continuous firing as long as the trigger is held down. This mode is typically used in military and tactical operations where a high volume of fire is needed to suppress enemy forces or provide cover for advancing troops. Fully automatic firearms are regulated by strict laws in many countries to prevent misuse and ensure public safety.
Selective-fire triggers are designed to switch between these different firing modes with a simple adjustment or manipulation. Some firearms feature a selector switch that allows the shooter to choose the desired mode, while others have a dual-stage trigger that can be pulled in different ways to activate different modes. Understanding how these triggers work is essential for safe and effective use of firearms in various situations.
Applications of selective-fire triggers in firearms are diverse and varied, ranging from recreational shooting to military operations. In civilian settings, selective-fire triggers are often used for target practice, competitive shooting, and hunting. These triggers allow shooters to customize their firearms to suit their preferences and shooting style, enhancing their overall shooting experience.
In law enforcement and security settings, selective-fire triggers are used to provide officers with the flexibility to respond to different threats effectively. By switching between semi-automatic, burst fire, and fully automatic modes, law enforcement officers can adapt to changing situations and engage targets with precision and efficiency. Selective-fire triggers are also used in specialized units such as SWAT teams and tactical response teams to handle high-risk operations with speed and accuracy.
In military applications, selective-fire triggers play a crucial role in modern warfare by providing soldiers with the ability to engage targets at different ranges and in various combat scenarios. By selecting the appropriate firing mode, soldiers can maximize their firepower and effectiveness on the battlefield, giving them a tactical advantage over their adversaries. Selective-fire triggers are integrated into a wide range of firearms, including rifles, machine guns, and submachine guns, to meet the diverse needs of military forces around the world.
Overall, understanding the mechanism and applications of selective-fire triggers in firearms is essential for anyone who uses or handles firearms regularly. By knowing how these triggers work and how they can be used in different situations, shooters can make informed decisions when selecting firearms and accessories for their specific needs. Whether for recreational shooting, law enforcement, or military operations, selective-fire triggers are a versatile and valuable tool that enhances the performance and capabilities of firearms in a wide range of applications.



